




2-IN-1 Integrated Machine Water Filteration mixed together water Softener
| Min. Order: | 12 Piece/Pieces |
|---|---|
| Trade Term: | FOB,CFR,CIF,EXW |
| Payment Terms: | Paypal, L/C, T/T, WU, Money Gram |
| Supply Ability: | 10000per month |
| Place of Origin: | Zhejiang |
Company Profile
| Location: | Ningbo, Zhejiang, China (Mainland) |
|---|---|
| Business Type: | Manufacturer, Trading Company |
Product Detail
| Model No.: | SF-P3 |
|---|---|
| Means of Transport: | Ocean, Land |
| Type: | Ion Exchange Resin (Water Softener) |
| Installation: | Cabinet |
| Classification: | Water Softener |
| Certification: | CE |
| Brand Name: | NATURE WATER/KEMAN |
| Capacity: | 25L |
| Power: | 12W |
| Voltage: | 110v /220v |
| Resin volume: | 25L |
| Good's Net Height: | 1102mm |
| FRP tank size: | 1035 |
| flow capacity: | ≤2.5T/H |
| Resin Brand: | Purolite C100EFG |
| Backwash Pre-purifier: | Auto flush Double SS net |
| Advantage: | Save room and cost |
| Production Capacity: | 10000per month |
| Packing: | 1pc/carton |
| Delivery Date: | 20days |
Product Description
Product Description
Automatic water softener +reusable doubel stage SS304 filter net water purifier
Auto Washing(forward and reverse flush)
Compact water softening
Food grade resin and SS304
Water softener, water softening system, water soften equipment
Extended service life of household appliance, such as water heater, boiler, shower, faucets,
Cleaner, softer clothes and towels
Keeping hair smooth and skin delicate
Keeping clear fineness tableware and sanitary hardware clearer, taste and oder- free ice cubes.
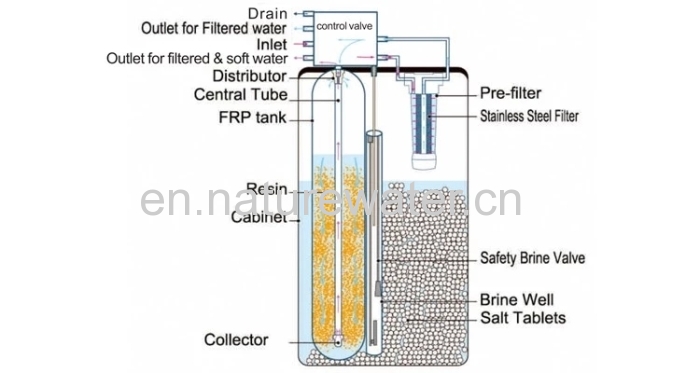
| Valve Type: | Electronic Softener Valve |
| Regeneration Mode: | Timer or Flowmeter |
| Resin Volume: | 25L |
| Filter | Double stage SS304 filteration |
| Brine Well Size: | 50KG |
| Resin Tank: | 1035 |
| Flow Rate: | ≤ 2.5T/H |
| Working Pressure: | 0.15-0.5 Mpa |
| Power Supply: | 110-220V 50/60Hz |
| Inlet/Outlet Size: | 1/2" ,3/4" ,1" |
| Drain Size: | Φ 12mm |
| Central Tube Size: | 35" |
| Brine Valve: | Yes |
| Weight(without salt): | ≤ 46KG |
| Cabinet Size(W*D*H): | 570X392X1102mm |
| Packing Size(W*D*H): | 665X475X1200mm |
| Container Capacity(20' GP/40' GP): | 170CTNS/320CTNS |
2 IN 1 Advantage New automatic softener filter
1. Central water purification and central water softener in one cabinet.
2. Large flowrate realizing water treatment of whole house.
3. Double outlets of purified water( pretreated water)and softened water for living using.
4. Designed with the visualized window for easily checking the salt capacity freely.
5. The design of touch control enables a better looking and more convenient operation.
2 IN 1
One machine offer dual purified water and softened water for living using, effectively saving space and cost of maintaining the product.










Hard water
1.1 What is hard water?
When water is referred to as 'hard' this simply means, that it contains more minerals than ordinary water. These are especially the minerals calcium and magnesium. The degree of hardness of the water increases, when more calcium and magnesium dissolves.
Magnesium and calcium are positively charged ions. Because of their presence, other positively charged ions will dissolve less easily in hard water than in water that does not contain calcium and magnesium.
This is the cause of the fact that soap doesn't really dissolve in hard water.
1.2 Which industries attach value to hardness of water?
In many industrial applications, such as the drinking water preparation, in breweries and in sodas, but also for cooling- and boiler feed water the hardness of the water is very important.
2. Water softening
2.1 What is water softening?
When water contains a significant amount of calcium and magnesium, it is called hard water. Hard water is known to clog pipes and to complicate soap and detergent dissolving in water.
Water softening is a technique that serves the removal of the ions that cause the water to be hard, in most cases calcium and magnesium ions. Iron ions may also be removed during softening.
The best way to soften water is to use a water softener unit and connect it directly to the water supply.
2.2 What is a water softener?
A water softener is a unit that is used to soften water, by removing the minerals that cause the water to be hard.
2.3 Why is water softening applied?
Water softening is an important process, because the hardness of water in households and companies is reduced during this process.
When water is hard, it can clog pipes and soap will dissolve in it less easily. Water softening can prevent these negative effects.
Hard water causes a higher risk of lime scale deposits in household water systems. Due to this lime scale build-up, pipes are blocked and the efficiency of hot boilers and tanks is reduced. This increases the cost of domestic water heating by about fifteen to twenty percent.
Another negative effect of lime scale is that it has damaging effects on household machinery, such as laundry machines.
Water softening means expanding the life span of household machine, such as laundry machines, and the life span of pipelines. It also contributes to the improved working, and longer lifespan of solar heating systems, air conditioning units and many other water-based applications.
2.4 What does a water softener do?
Water softeners are specific ion exchangers that are designed to remove ions, which are positively charged.
Softeners mainly remove calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions. Calcium and magnesium are often referred to as 'hardness minerals'.
Softeners are sometimes even applied to remove iron. The softening devices are able to remove up to five milligrams per litre (5 mg/L) of dissolved iron.
Softeners can operate automatic, semi-automatic, or manual. Each type is rated on the amount of hardness it can remove before regeneration is necessary.
A water softener collects hardness minerals within its conditioning tank and from time to time flushes them away to drain.
Ion exchangers are often used for water softening. When an ion exchanger is applied for water softening, it will replace the calcium and magnesium ions in the water with other ions, for instance sodium or potassium. The exchanger ions are added to the ion exchanger reservoir as sodium and potassium salts (NaCl and KCl).
2.5 How long does a water softener last?
A good water softener will last many years. Softeners that were supplied in the 1980's may still work, and many need little maintenance, besides filling them with salt occasionally.
3. Softening salts
3.1 Which types of salt are sold for application in a water softener?
For water softening, three types of salt are generally sold:
- Rock salt
- Solar salt
- Evaporated salt
Rock salt as a mineral occurs naturally in the ground. It is obtained from underground salt deposits by traditional mining methods. It contains between ninety-eight and ninety-nine percent sodium chloride. It has a water insolubility level of about 0.5-1.5%, being mainly calcium sulphate. Its most important component is calcium sulphate.
Solar salt as a natural product is obtained mainly through evaporation of seawater. It contains 85% sodium chloride. It has a water insolubility level of less than 0.03%. It is usually sold in crystal form. Sometimes it is also sold in pellets.
Evaporated salt is obtained through mining underground salt deposits of dissolving salt. The moisture is then evaporated, using energy from natural gas or coal. Evaporated salt contains between 99.6 and 99.99% sodium chloride.
3.2 Should we use rock salt, evaporated salt or solar salt in a water softener?
Rock salt contains a lot of matter that is not water-soluble. As a result, the softening reservoirs have to be cleaned much more regularly, when rock salt is used. Rock salt is cheaper than evaporated salt and solar salt, but reservoir cleaning may take up a lot of your time and energy.
Solar salt contains a bit more water-insoluble matter than evaporated salt. When one makes a decision about which salt to use, consideration should be given to how much salt is used, how often the softener needs cleanout, and the softener design. If salt usage is low, the products could be used alternately.
If salt usage is high, insoluble salts will build up faster when using solar salt. Additionally, the reservoir will need more frequent cleaning. In that case evaporated salt is recommended.
3.3 Is it harmful to mix different kinds of salt in a water softener?
It is generally not harmful to mix salts in a water softener, but there are types of softeners that are designed for specific water softening products. When using alternative products, these softeners will not function well.
Mixing evaporated salt with rock salt is not recommended, as this could clog the softening reservoir. It is recommended that you allow your unit to go empty of one type of salt before adding another to avoid the occurrence of any problems.
3.4 How often should one add salt to a softener?
Salt is usually added to the reservoir during regeneration of the softener. The more often a softener is regenerated, the more often salt needs to be added.
Usually water softeners are checked once a month. To guarantee a satisfactory production of soft water, the salt level should be kept at least half-full at all times.
3.5 How come water sometimes does not become softer when salt is added?
Before salt starts working in a water softener it needs a little residence time within the reservoir, since the salt is dissolving slowly. When one immediately starts regeneration after adding salt to the reservoir, the water softener may not work according to standards.
When the water softening does not take place it could also indicate softener malfunction, or a problem with the salt that is applied.

