





RP HP UHP Grade Graphite Electrode 350mm 300mm 250mm 200mm Graphite Electrodes with 3tpi 4tpi Nipples
| Min. Order: | 20 Ton |
|---|---|
| Trade Term: | FOB,CFR,CIF,DAT,FAS,DDP,DAP,CIP,CPT,FCA,EXW |
| Payment Terms: | Paypal, L/C, D/P, D/A, T/T, WU, Money Gram |
| Supply Ability: | 80000 Ton/Year |
| Place of Origin: | Hebei |
Company Profile
| Location: | Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China (Mainland) |
|---|---|
| Business Type: | Manufacturer |
Product Detail
| Model No.: | Graphite Products |
|---|---|
| Means of Transport: | Ocean, Air, Land |
| Brand Name: | BENHONG |
| Type: | Graphite Electrodes |
| Composition: | Graphite, Needle BCK , Petroleum BCK |
| Carbon Content: | High-Carbon |
| Forming Way: | Molded Graphite |
| Modulus of Rupture: | 10-14 MPa |
| Ash: | 0.3% |
| Length: | 1500-2700mm |
| Resistivity: | 4.6-5.8 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.68-1.74 g/cm3 |
| Transport Package: | Wooden Pallets with Steel Strips |
| Production Capacity: | 80000 Ton/Year |
| Packing: | Graphite Electrodes are packed on wooden pallets |
| Delivery Date: | negotiate |
Product Description
DESCRIPTION
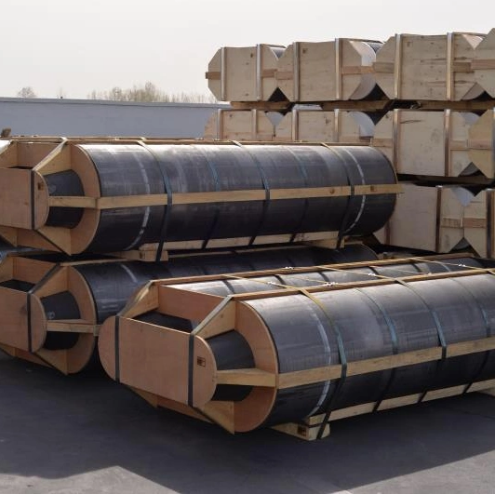


UHP graphite electrode is used for the recycling of steel in the electric arc furnace industry. Its main ingredient is high-value needle bck which is made from either petroleum or coal tar. Graphite electrodes are finished with a cylinder shape and machined with threaded areas at each end. In this way, the graphite electrodes can be assembled into an electrode column using electrode nipple.
In order to meet the requirement of higher work efficiency and lower total cost, large capacity ultra-high power arc furnaces are becoming more and more popular. Because of this, UHP graphite electrodes with diameters of over 500 mm will dominate market.
FEATURE
Withstand large currents, high discharge rate.Good dimension stability, not easy to deform.Resistant to bursting & spalling.High resistance to oxidation and thermal shock.High mechanical strength, low electrical resistance.High machining accuracy, good surface finishing.
APPLICATION
Graphite electrodes are widely used for production of alloy steels, metal and other nonmetallic materials, etc.DC electric arc furnace.AC electric arc furnace.Submerged arc furnace.Ladle furnace.
SPECIFICATION
Table 1: Technical Specification of UHP Graphite Electrode
Resistance | Density | FlexureStrength | ElasticModulus | AshContent | CTE | CurrentLoad | CurrentDensity | |
(inch) | (≤,µ·m) | (≥,g/cm3) | (≥,MPa) | (≤,GPa) | (≤,%) | (100°C-600°C) | (A) | (A/cm2) |
(≤,10-6/°C) | ||||||||
10 | 14 | 8100-12200 | 20-30 | |||||
12 | 14 | 15000-22000 | 20-30 | |||||
14 | 14 | 20000-30000 | 20-30 | |||||
16 | 14 | 25000-40000 | 19-30 | |||||
18 | 14 | 32000-45000 | 19-27 | |||||
20 | 11 | 14 | 38000-55000 | 18-27 | ||||
22 | 11 | 14 | 42000-66000 | 17-26 | ||||
24 | 11 | 14 | 49000-76000 | 17-26 |
Table 2: Graphite Electrode Size & Tolerance
Diameter(mm) | Length(mm) | ||||||
NominalDiameter | ActualDiameter | NominalLength | Tolerance | ShortLength | |||
(inch) | (mm) | (max.) | (min.) | (roughspot) | |||
10 | 250 | 256 | 251 | 248 | 1600/1800 | ±100 | -275 |
12 | 300 | 307 | 302 | 299 | 1600/1800 | ||
14 | 350 | 357 | 352 | 349 | 1600/1800 | ||
16 | 400 | 409 | 403 | 400 | 1600/1800/2000/2200 | ||
18 | 450 | 460 | 454 | 451 | 1600/1800/2000/2200 | ||
20 | 500 | 511 | 505 | 502 | 1800/2000/2200/2400 | ||
22 | 550 | 562 | 556 | 553 | 1800/2000/2200/2400 | ||
24 | 600 | 613 | 607 | 604 | 2000/2200/2400/2700 | ||
SURFACE QUALITY
There should be less than two defects or holes on the electrode surface, the maximum size of which is mentioned in the below chart.There should be no transverse burst on the electrode surface. For the longitudinal burst, the length should be less than 5% of the electrode circumference and the width should be 0.3 to 1.0 mm.The width of black area on electrode surface should be less than 1/10 of the electrode circumference and the length should be less than 1/3 of the electrode.
SpecificationDefectDimension | NominalDiameterofGraphiteElectrode(mm) | |
300-400 | 450-600 | |
Diameter(mm) | 20-40 | 30-50 |
(<20mmshouldbenegligible) | (<30mmshouldbenegligible) | |
Depth(mm) | 5-10 | 10-15 |
(<5mmshouldbenegligible) | (<10mmshouldbenegligible) | |
Guidance of Using
Being hard and brittle ,artificialgraphite electrode shall be specially handled.Proper operationg may reduce the consumption and cost.
1. Professional tools should be used for hoisting graphite electrodes. It is strictly forbidden to use a crowbar to prevent impact damage during handling.
2. Graphite electrodes are prohibited from rain, snow and water, and should be kept dry. If it is found to be damp, it should be dried before use, the temperature should not exceed 100 ºC, and the drying time should not be less than 48h.
3. Do not stack near debris such as clay, slag, etc., so as not to pollute the surface of the graphite electrode and affect the conductive effect.
4. Before the graphite electrode is connected, carefully check whether the electrode connector hole is intact, whether the connector thread is damaged, and whether the connector bolt is lost. When the electrode is lifted, the electrode connector thread of the ground terminal should be prevented from being damaged.
5. Dust and debris in the joints and joint holes should be blown dry with compressed air.
6. Graphite electrodes must be tightly connected, and no tilt is allowed during connection. Torque wrenches should be used to prevent excessive force or too small, and the gap is not greater than 0.4mm.
7. The electrode holder should be clamped, not loose and in good contact, and no arc should be generated. Otherwise, the connection will be reddish, oxidized, thinned and broken.
8. If the electrode is lifted with a metal lifting plug, the thread in the joint hole must not be damaged. After lifting, the lifting plug should be unscrewed to prevent dust and debris from falling into the joint hole.
9. When the electrode lifting device of the electric furnace is running, it should be kept stable. After the furnace cover is repaired, check whether the furnace cover is positioned correctly. During smelting, refractory materials are used to close the furnace lid to prevent the oxidation of the upper electrode of the flame in the furnace.
10. The holder should be clamped outside the safety wire of the electrode connector hole area.
11. When distributing the molten pool, the big piece is at the bottom and the small piece is at the top. Do not place the charge with poor conductivity on the top. During melting, the unmelted charge should be handled in time to prevent the collapsed material from breaking the electrode.



