
SWEP B25TH BRAZED PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER
| Min. Order: | 10 Piece/Pieces |
|---|---|
| Payment Terms: | L/C, T/T |
| Supply Ability: | 130000 units per month |
| Place of Origin: | Zhejiang |
Company Profile
| Location: | Ningbo, Zhejiang, China (Mainland) |
|---|---|
| Business Type: | Manufacturer |
Product Detail
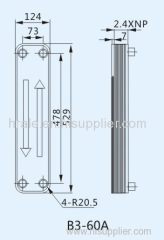
| Model No.: | B3-60A |
|---|---|
| Means of Transport: | Ocean, Air |
| Category: | Heat Exchanger |
| Capacity Type: | Light Duty |
| Certification: | CE |
| Brand Name: | HRALE |
| Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger: | Secondary Heat Exchanger for Gas Boiler |
| Production Capacity: | 130000 units per month |
| Packing: | Pallets |
| Delivery Date: | 20 days |
Product Description
HRALE B3-60A BRAZED PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER
| Technical parameter | |
| Product name | Flat Plate Heat Exchanger |
| Product model | B3-60A |
| Unit heat exchanging area | 0.060m2 |
| Maximum Flowrate | 22m3/h |
| Plate material | 316L or 304 stainless steel |
| Welding material | 99.9% copper |
| Thickness of plate | 0.4mm |
| Volume per channel | 0.111L |
| Maximum number of plate | 120 |
| Design pressure | 3.0MPa or 4.5MPa |
| Test pressure | 4.5MPa or 6.0MPa |
| Design temperature | -195 ~+220 |
| Connections | the biggest screw threads pipe for water: 5/4", the biggest welded pipe for other fluid : 15/8" |
| Refrigeration Capacity | 10-70KW |
| Basic Procedures | F1-> F3 F4-> F2 |
| Application scope | Heaing Industry, Heat Pump, Cetral Air-conditioning, Refrigeration Equipment, Industrial water cooler, oil cooler, etc. |
How Heat Transfer Works
Heat transfer occurs when there is a difference in temperature between two mediums. Heat will travel from the hot source to the cold source. The rate at which the heat transfer occurs at is determined by many factors such as the heat conductivity of the two materials andthe difference in temperatures of the two mediums. Convectiuve heat transfer occurs when the materials are moving against each other.
Plate heat exchangers have significantly good heat transfer rates because they use metal plates which have high heat conductivity rates and the plates are extremely thin. The plate heat exchangers also achieve high amounts of heat transfer through convective forces with both working fluids. With large temperature differentials, great amounts of heat transfer can be achieved using a plate heat exchanger.
Corrosion
Corrosion is usually how these units will fail. Use fluids with reasonable pH levels to ensure a long lasting life. Hard water will corrode faster than regular water. (Use distilled if possible; Distilled should never corrode it) Salt water will corrode stainless steel very fast. It is recommended to clean the exchanger often if you are using corrosive fluids. Normal usage (non-corrosive fluids) should expect 10-20 years of life. Fluids containing chlorides will corrode the unit quickly.
Applications
This is an extremely popular unit for wood burning furnaces, radiant floor systems, refrigerant systems, straight vegetable oil conversions, beer chilling, air conditioning system and solar water heating systems. It will work for any application in which the desired result is for two fluids (liquid or gas) to exchange heat.
How it Works
Fluid A passes from the port on the left of the heat exchanger through every other channel created by the plates to the opposite end port on the left of the heat exchanger (looking at it the long way). Fluid B passes from the port on the right through the other channels created by the plates and comes out the other port on the right side. The fluids are essentially touching each other through the plates and heat is transferred from the hot fluid to the cold fluid. (but the fluids do not mix)




.gif)

