

D-DIMER test assay (chemiluminescence assay)
| Min. Order: | 1000 Piece/Pieces |
|---|---|
| Trade Term: | FOB,CFR,CIF,DAT,FAS,DDP,DAP,CIP,CPT,FCA,EXW |
| Payment Terms: | Paypal, L/C, D/P, D/A, T/T, WU, Money Gram |
| Supply Ability: | 1,000,000.00/Month |
| Place of Origin: | Jiangsu |
Company Profile
| Location: | Nanjing, Jiangsu, China (Mainland) |
|---|---|
| Business Type: | Manufacturer |
Product Detail
| Model No.: | NRM-411 |
|---|---|
| Means of Transport: | Ocean, Air |
| Brand Name: | NORMAN |
| Brand Name: | Norman |
| Place of Origin: | Jiangsu, China (Mainland) |
| Means of Transport: | Ocean,Air |
| Packing: | In carton |
| Manufacture: | Independent R & D |
| Service: | International after-sales |
| Delivery Detail: | Depend on quantity |
| Delivery Date: | Two weeks after payment |
| Methodology: | chemiluminescence assay |
| Type: | NRM--411 |
| Production Capacity: | 1,000,000.00/Month |
| Packing: | IN CARTON |
| Delivery Date: | TWO WEEKS AFTER PAYMENT |
Product Description
D-DIMER reagent (chemiluminesence assay)

Methodology
chemiluminesence immunoassay(CLIA)
D-Dimer
Negative exclutionindex of venous thromboembolism
High sensitivity, VTE negative predictive value ≥99%, significantly reduce misdiagnosis rate.
One of the earlist D-dimer kits utilizingchemiluminescence methodology, leading the
direction of high sensitivity D-dimer test direction.
D-Dimer Definition
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a fibrin degradation product (or FDP), a small protein fragment
present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because
it contains two crosslinked D fragments of the fibrin protein.
D-dimer concentration may be determined by a blood test to help diagnose thrombosis.
Since its introduction in the 1990s, it has become an important test performed in patients
with suspected thrombotic disorders. While a negative result practically rules out
thrombosis, a positive result can indicate thrombosis but does not rule out other potential
causes. Its main use, therefore, is to exclude thromboembolic disease where the probability
is low.
In addition, it is used in the diagnosis of the blood disorder disseminated intravascular
coagulation.
Principles of D-Dimer
Coagulation, the formation of a blood clot or thrombus, occurs when the proteins of
the coagulation cascade are activated, either by contact with damaged blood vessel
wall and exposure to collagen in the tissue space (extrinsic pathway) or by activation
of factor VII by tissue activating factors (intrinsic pathway). Both pathways lead to
the generation of thrombin, an enzyme that turns the soluble blood protein fibrinogen
into fibrin, which aggregates into proteofibrils. Another thrombin-generated enzyme,
factor XIII, then crosslinks the fibrin proteofibrils at the D fragment site, leading to
the formation of an insoluble gel which serves as a scaffold for blood clot formation.
D-dimers are not normally present in human blood plasma, except when the coagulation
system has been activated, for instance because of the presence
of thrombosis or disseminated intravascular coagulation. The D-dimer assay depends
on the binding of a monoclonal antibody to a particular epitope on the D-dimer fragment.
Several detection kits are commercially available; all of them rely on a different monoclonal
antibody against D-dimer. For some of these, the area of the D-dimer to which the
antibody binds is known. The binding of the antibody is then measured quantitatively by
one of various laboratory methods.
For DVT and PE, there are possible various scoring systems that are used to determine
the a priori clinical probability of these diseases; the best-known is the Wells score.
Interpretation
Reference ranges
Following are reference ranges for D-dimer
UnitsNonpregnant
adultFirst trimesterSecond trimester Third trimester
| Units | Nonpregnant adult | First trimester | Second trimester | Third trimester |
| mg/L or µg/mL | < 0.5 | 0.05 - 0.95 | 0.32 - 1.29 | 0.13 -1.7 |
| µg/L or ng/mL | < 500 | 50 - 950 | 320 - 1290 | 130 - 1700 |
| nmol/L | < 2.7 | 0.3 - 5.2 | 1.8 - 7.1 | 0.7 - 9.3 |
Indications of D-Dimer
D-dimer testing is of clinical use when there is a suspicion of deep venous
thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism(PE) or disseminated intravascular
coagulation (DIC).It is under investigation in the diagnosis of aortic dissection.
Clinical Significance
Deep vein thrombosis (DVI) and exclusion diagnosisof pulmonary embolism(PE).
Diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation(DIC)
Effective detection and evaluation indicator of thrombolytic effect.
Condition evaluation of cardiovascular disease
Identification and treatment detection of cerebral infarction.
Applicable Department
ICU, outpatient emergency, surgery, Department of respiration, Department of
Cardiology, Internal Medicine-Neurology,Geriatric department, oncology, gynecology.
Product Advantage
1.High sensitivity:50ng/ml
2.High accuracy:99% result correlation with Siemens INNOVANCE D-dimer
3.Wide linear range: 50-10000ng/ml(FEU)
Correlation analysis between Norman D-Dimer and Siemens INNOVANCE D-Dimer
European society of Cardiology
Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute pulmonary embolism
Recommend to use D-dimer testing as the screening indicator of pulmonary
embolismdiagnosis in emergency department
Clinical and laboratory standards institute
H59-P guideline: In low and middle clinical risk peak, D-dimer quantitive testing is used
for excluding diagnosis of Venous Thrombus Embolism(VET).
Product Show


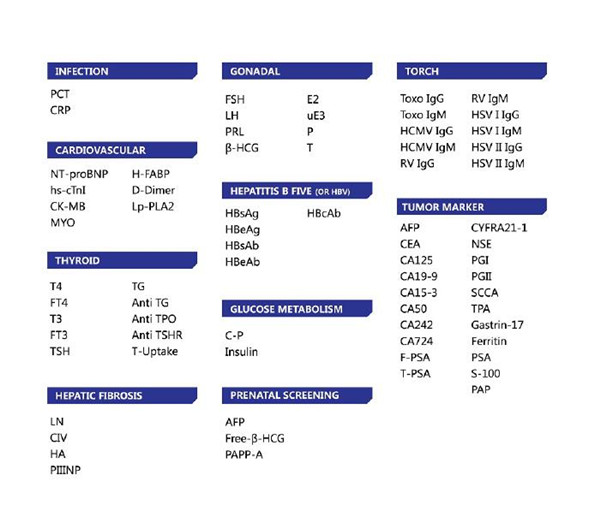
Related Reagents
About us
Powered by advanced technology and excellent talents in the IVD field, Norman has been
consistently improving its innovation platform , and increasing R&D investment. Self-
innovation, combined with long-term strategic cooperation with universities and research
institutes and with outsourced technologies, ensures consistent improvement on product
quality. Norman's R&D field has covered instruments, reagents, and raw materials, and
has been entrusted by the Nanjing government to build a R&D center specialized in
biological chemistry and immunity diagnosis. Up to now, Norman has acquired over 20
patents.


Being an expert in automated chemiluminescence analysis , Norman owns independent and
completed intellectual property rights, and its products provide top-notch sensitivity,
precision and accuracy . Thanks to the self-developed antigens and self-manufactured
antibodies, Norman's products features minimized intra-and inter- batch difference.
After 8 years development, Norman is now on the fast track. An over 30,000m2 global
R&D center is in construction, and will hold more than 1,000 R&D engineers in the future.

Agent Wanted
If you are interested in working with us, please feel free to contact.







