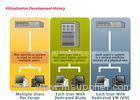
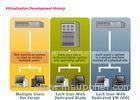
Distributed Government Cloud Computing Desktop Virtualization VDI VS OS Streaming
| Place of Origin: | Zhejiang |
|---|
Company Profile
| Location: | Wuhan, Hubei, China (Mainland) |
|---|---|
| Business Type: | Manufacturer |
Product Detail
| Model No.: | VDI v4 |
|---|
Product Description
Distributed Government Cloud Computing Desktop Virtualization VDI VS OS Streaming
Distributed virtual desktops
A distributed desktop model lets you deploy different desktop images to a specific group of users based on their location or job function. This type of model can be useful if you have a number of different types of users in a single location or users in a variety of locations, such as branch offices.
Each group has different desktop requirements or is connected by a slow or intermittent link. The remote users may have a file server that stores their files and information.
The pre-boot execution environment (PXE) is another distributed desktop design. This method lets you deploy an image to a server and a desktop to download and boot that image at startup. You can develop and deploy several desktop images and have them assigned to a certain desktop or group of desktops. When the user starts that desktop, the image is streamed to the device as it starts up. Changing a desktop image is as simple as reconfiguring the device’s target image and restarting the desktop.
This is a viable design if you have to run applications from the local desktop. Some applications require a hardware key or a specific MAC address for licensing. Applications that require special graphics or additional cards or adapters not supported in a virtual environment are also good candidates for this type of deployment.
The drawbacks and benefits are as follows:
1. You have to load the individual images with any applications or drivers required for the individual desktop computers. Unless all the desktops are identical, you may need to add different drivers required for each type of hardware for which the image is being prepared.
2. You can configure a different image to load on a desktop as a shift changes or new updates are configured. This is particularly useful because a new image is loaded each time the desktop is rebooted. Viruses and malware are limited in their effectiveness because the entire desktop image is reloaded each time the desktop is reloaded.
3. The VDI image is received from the primary datacenter. The management station controls which images are assigned to the local and remote users. Local users connect to the image assigned to them from the VDI server in the datacenter.
4. This model is best used with a local server that holds the desktop images. Loading a desktop image over a WAN is a slow process that will discourage remote users from rebooting their desktops. In this scenario, you should look at using either a local VDI or a distributed VDI solution.
3. Desktop virtualization & OS streaming Comparison
|
|
Items |
Desktop Virtualization (VDI) |
OS streaming |
|
Technology |
Principle |
Virtualization technology separates Operating System, application and data from hardware, which allows users to get the desktop screen and interactive experience in any device and any network. |
Client running Operating System images are stored in server. Terminal bootable chip get the required image from server. After terminal finished downloading the booting data, the system control right switches from Boot ROM to certain special area in memory, and boot the operating system for normal using. |
|
VDI separates hardware and software |
OS streaming does not separate |
||
|
Virtual isolation technology. |
Image snapshot technology from ghost era. |
||
|
No need to start the NIC |
Terminal must has boot NIC, boot from RPL and PXE. |
||
|
Server side |
Auto adjust hardware resources |
Auto adjusts CPU, RAM resource from one unused desktop to running desktop. |
Can not |
|
Terminal |
Terminal support |
All desktops are running on server, terminal is just interactive interface. |
Actually use terminal hardware to run image. More hardware investment. |
|
Not only use old PC, laptops, thin clients, all in one PC with X86 terminals, but also use ARM box, PAD and other lower-cost terminals; |
High-spec requirement for clients’ hardware, use PC or costly high-spec X86 architecture. |
||
|
· ARM terminal is more energy saving and environmental protection, longer lifecycle |
X86 hardware terminals will be eliminated every three years |
||
|
ARM terminal with lower-power consumption |
X86 terminal with higher-power consumption |
||
|
Supports Wireless |
Unable to support Wireless |
||
|
Supports handheld terminals |
unable to support |
||
|
Terminal device Maintenance |
Maintenance-free for terminals |
Hardware parts has the same maintenance problems like traditional PC |
|
|
Hardware Compatibility |
All hardware is isolated by virtualization, use virtual machine, so no terminal hardware compatibility problems, you can run virtual machines on any platform. |
Different terminal hardware specification required to prepare different image drive, poor drive compatibility. |
|
|
Support different spec terminal |
Virtual machines run on the server side, different terminal devices do not affect the use of virtual machines on server. |
Different spec terminals require preparing different disk images, poor flexibility. |
|
|
Deploy and Update |
Deployment |
Use Link Clone technology, a desktop deployment takes 1-2 seconds |
Slow deployment, each terminal needs to boot image by LOCAL CACH |
|
Update in batch |
fast speed, supports a key to update |
|

