Fenvalerate
| Place of Origin: | Shanghai |
|---|
Company Profile
| Location: | China (Mainland) |
|---|---|
| Business Type: | Manufacturer, Trading Company |
Product Detail
| Model No.: | 51630-58-1 |
|---|
Product Description
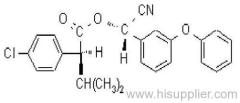
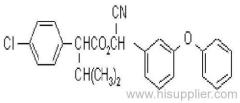
Common name: fenvalerate
IUPAC name: (RS)-a-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (RS)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutyrate
Chemical Abstracts name: cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl 4-chloro-a-(1-methylethyl)benzeneacetate
CAS RN: [51630-58-1] unstated stereochemistry
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition: Tech. grade fenvalerate is 92% pure. Mol. wt.: 419.9; M.f.: C25H22ClNO3; Form: Tech. fenvalerate is a viscous yellow or brown liquid, sometimes partly crystalline at room temperature. M.p.: 39.5-53.7 °C (pure). B.p.: Decomposes on distillation. V.p.: 1.92x10-2 mPa (20 ºC). KOW: logP = 5.01 (23 ºC). S.g./density: 1.175 (25 ºC). Solubility: In water <10 ug/l (25 ºC). In n-hexane 53, xylene 200, methanol 84 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability: Stable to heat and moisture. Relatively stable in acidic media, but rapidly hydrolysed in alkaline media. F.p.: 230 °C.
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action: Non-systemic insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action.
Uses: Control of a wide range of pests, including those resistant to organochlorine, organophosphorus, and carbamate insecticides. Uses include control of chewing, sucking, and boring insects (particularly Lepidoptera, Diptera, Orthoptera, Hemiptera, and Coleoptera) in fruit, vines, olives, hops, nuts, vegetables, cucurbits, cotton, oilseed rape, sunflowers, alfalfa, cereals, maize, sorghum, potatoes, beet, peanuts, soya beans, tobacco, sugar cane, ornamentals, forestry, and on non-crop land. Used for control of flying and crawling insects in public health situations and in animal houses. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide.
Formulation types: EC; UL; SC; WP.
Compatibility: Incompatible with alkaline materials.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral: Acute oral LD50 for rats 451 mg/kg.
Skin and eye: Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 1000-3200, rats >5000 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits).
Inhalation: LC50 for rats >101 mg/m3.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats 250 mg/kg diet.
ADI: 0.02 mg/kg b.w.
Toxicity class: WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds: Acute oral LD50 for domestic fowl >1600, mallard ducks 9932 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for quail >10 000, mallard ducks 5500 mg/kg.
Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.0036 mg/l.
Bees: Toxic to bees. Contact LD50 0.23 ug/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals: In mammals, following oral administration, fenvalerate is rapidly metabolised. Up to 96% is excreted in the faeces within 6-14 days. For a study of the metabolism of fenvalerate in the laying hen.
Plants: In plants, fenvalerate is split into two parts by cleavage of the ether group, followed by further hydroxylation in the 2- and 4- positions of the phenoxy ring, and hydrolysis of the nitrile group to amide and carboxyl groups. The majority of the acids and phenols thus formed are converted into glucosides.
Soil/Environment: In aqueous media, the ester bond is hydrolysed. In light, decarboxylation occurs, with recombination of the cleaved moieties. DT50 in soil c. 75-80 d.